In 2017, Mauritius was the highest ranked country in the African region according to the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI), ranking sixth in the world. Our country is particularly well placed in the legal and technical fields, two of the pillars of the survey, which is a barometer to assess the level of commitment of Member States in the fight against cybercrime.
This first place proves that the issue of security has been placed high on the Mauritian government’s agenda. The GCI survey is conducted by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) to measure the commitment of member states to cyber security, with the aim of raising awareness among IT companies worldwide.

The GCI 2017 highlights that the Mauritius Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-MU), can take proactive measures to mitigate threats on various networks across the country. For this purpose, it has a Botnet monitoring and detection project. According to one report, capacity building is also an area in which Mauritius seems to excel. Incidentally, the 2017 GCI recalls that the Government Information Security Unit conducted 180 awareness sessions for some 2,000 civil servants across 32 government ministries and departments.
Top 10 of the Global Cybersecurity Index
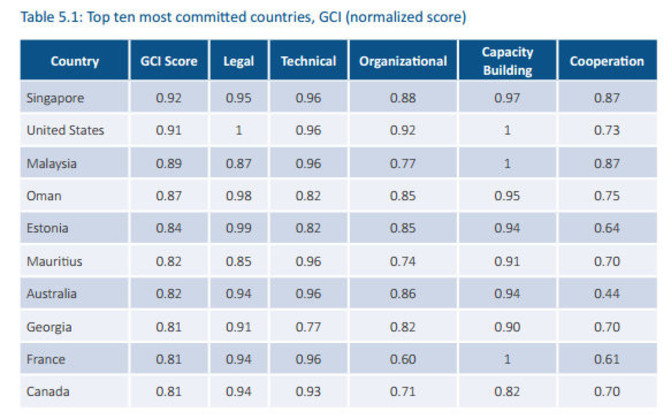
The top 10 countries in this global ranking are: Singapore (0.925); United States (0.919); Malaysia (0.893); Oman (0.871); Estonia (0.846); Mauritius (0.820); Australia (0.824); Georgia (0.819) and France (0.819) (tied); Canada (0.818); and Russia (0.788).
Three categories were used to classify the Member States:
- Initiating Stage for 96 countries that have begun to make cybersecurity commitments,
- Maturing Stage for 77 countries that have developed complex commitments and participated in cyber security programs and initiatives,
- Leading Stage for 21 countries that demonstrate high commitment to the five pillars of the index.
Mauritius stands out in the Leading Stage category.
Rwanda and Kenya are also on the podium
Mauritius is not the only African country to have distinguished itself in this ranking. Rwanda ranks second in Africa and 36th in the world, thanks to several bilateral and multilateral agreements on cyber security cooperation.
Kenya, which ranks third in Africa and 45th in the world, scores high on the organizational pillar. The country of a thousand hills has adopted an autonomous cyber security policy that takes into account both the public and private sectors. It also committed to developing a more resilient cyber security sector to strengthen its cyber space.

About the Global Cybersecurity Index
Launched in 2014, the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) aims to promote a global culture of cyber security and its integration into the core of ICT. The GCI 2017, which is the second edition, measures the commitment of ITU member states to cyber security in order to stimulate efforts for its global adoption and integration. The IAG is commenting on ITU’s global cyber security agenda and its five pillars (legal, technical, organizational, capacity building and cooperation). For each of these pillars, questions have been developed and sent to Member States to assess their commitment to this.



